What is Underground Drainage?
Underground drainage is essentially what its name implies—a drainage system located beneath the surface. It's typically composed of various lengths of pipes along with fittings like bends, junctions, and other components designed to adjust the direction or adapt to other systems. This type of drainage is mostly associated with sewage systems, primarily used to transport wastewater (gray water) or foul water directly to a sewage treatment plant. Additionally, it can also be utilized for rainwater drainage into a soakaway system or watercourse.
These days, the systems are predominantly made from PVC due to its lightweight yet durable nature, which ensures longevity and cost-effectiveness compared to materials like clay or concrete. Its lightweight characteristic makes installation simpler, and it requires minimal maintenance. The smooth inner walls enhance the flow of wastewater, providing a better flow rate than clay or concrete.
One distinguishing feature of underground drainage systems is their terracotta color, which is the industry standard. Interestingly, soil pipes and fittings are similar in construction but are colored black, white, or gray with a UV additive to prevent discoloration from sunlight exposure.
How do you install underground drainage?
First, the trenches need to be dug to the appropriate "fall" (using gravity to move the wastewater), then lined with pea shingle (usually 10mm or 20mm) to protect the pipework. The layout must also account for rodding, testing, cleaning, and inspecting the system.
An underground drainage installation is usually planned by a drainage engineer with architectural plans, but for smaller tasks, the system can be installed by a groundworker or general builder as long as it adheres to the requirements of Approved Document H – Drainage and Waste Disposal.
Joining the fittings and pipework is straightforward. They are typically a "push fit" system where the pipes come with sockets that include a rubber seal, and the fittings come with either a spigot (fits into another fitting or pipe socket) or a socket (accepts a spigot).

Â
How do I cut and join the pipework?
Cutting the pipe is simple with a hacksaw or fine-toothed saw, but leaving the end rough or sharp can damage the seal during joining, leading to leaks—especially problematic with foul water. To avoid this, the pipe end should be chamfered using a chamfer tool to smooth it out. The seal in the socket should then be lubricated with proper pipe lubricant. After ensuring the pipe is aligned with the socket, push it in firmly until it stops, then pull back 10mm to allow for movement and expansion—your joint is now complete. This method is much easier than working with clay or concrete systems!
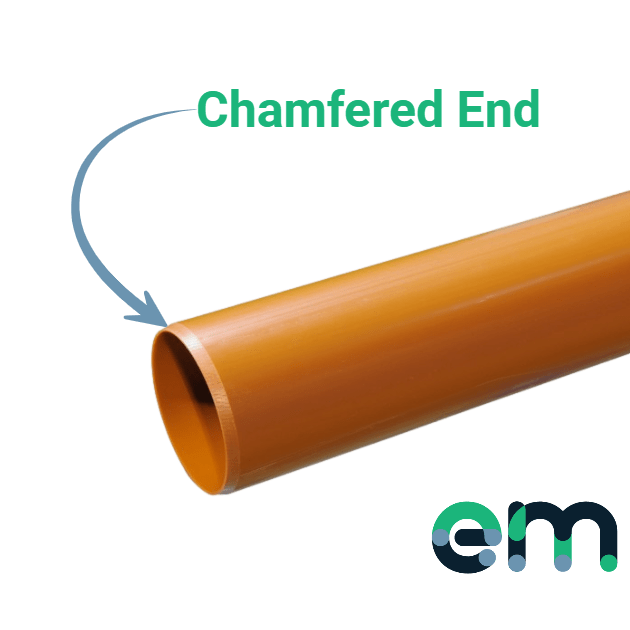
How to lay the underground pipes?
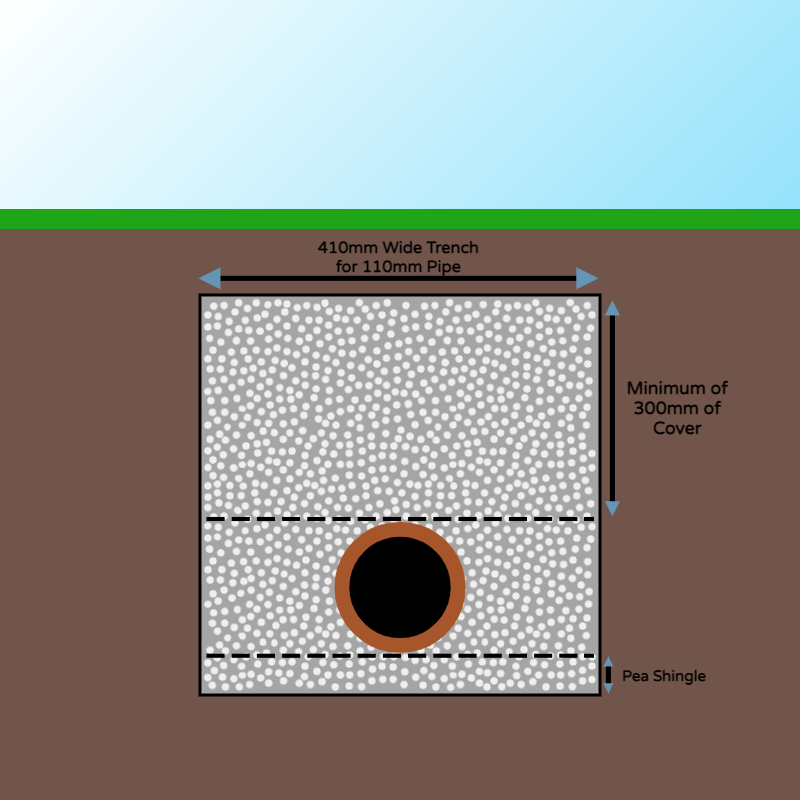
Best practices involve digging the trench, laying pea shingle (10mm/20mm) at the bottom, placing the drainage pipe over it, and filling the trench with more pea shingle to surround the pipe. This protects and supports the pipework while allowing for expansion and ground movement. For 110mm drainage pipe, the trench should be 410mm wide, and for 160mm, 460mm wide. The trench should always be 300mm wider than the pipe being laid. Using the excavated soil as backfill is possible but should be screened for large stones and isn't as protective as pea shingle.
When burying the pipework, a minimum of 300mm of cover should be placed over the top to prevent damage during soil compaction.
In areas where the pipework is likely to be dug up again, it’s good practice to place a paving slab over the top to protect the pipe from tools like spades or shovels. Warning tapes labeled “caution sewer pipe below†can also be installed to alert diggers of the pipes beneath.
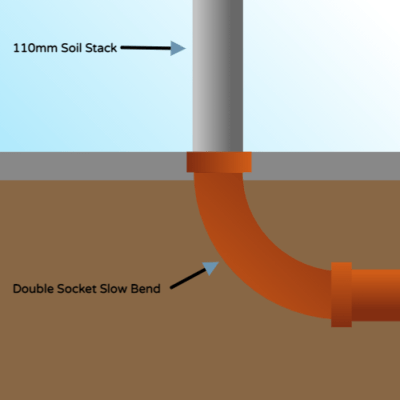
How does it connect to the above ground system?
As mentioned earlier, the soil pipe systems (110mm black, white, or gray pipes running down the side of the house into the underground system) are nearly identical and made using the same machines. Therefore, the cutting and joining process remains the same, and specialized adapters are rarely needed.
Rainwater pipes or waste pipes, however, differ slightly in size. For rainwater downpipes, a rubber rainwater adaptor is necessary. Push this into the 110mm underground pipe, then push the downpipe into it. The same adapter can also be used for waste pipe systems, though waste pipes are usually connected to the 110mm soil pipe higher up the run. Various adapters made from PVC are available in different colors to match the downpipe.
What fittings are commonly used in the underground drainage system?
- Underground Drainage Pipe – These come in 3m or 6m lengths and often include a socket on the end for easy connection of multiple pipes without additional couplers or joiners.
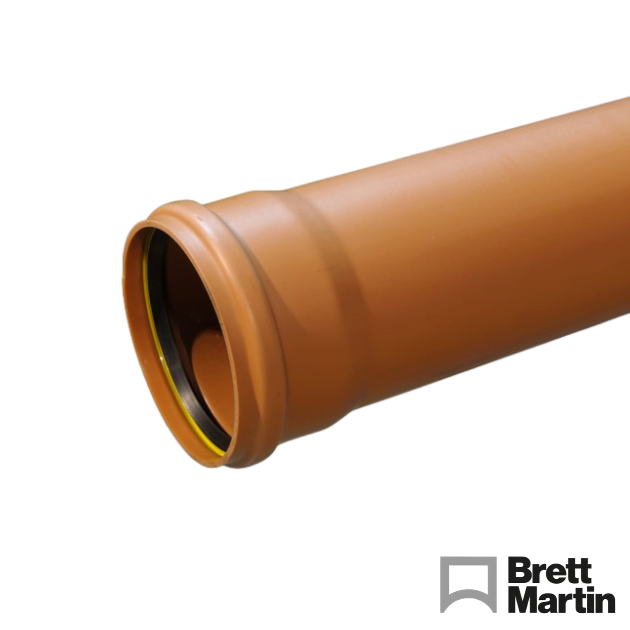

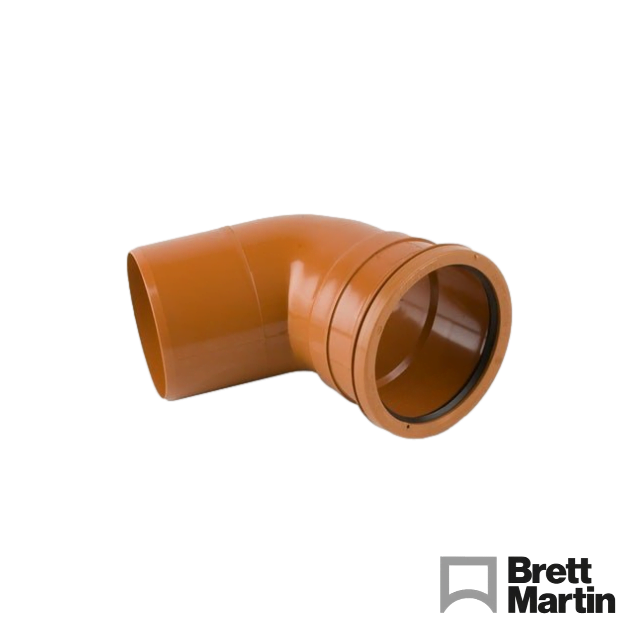
- Drainage Pipe Bends – Used to change the direction of the pipe run, they come in different angles from 11.25 to 90 degrees. Available as single socket (spigot on one end, socket on the other) or double socket (two sockets, no spigot). Adjustable bends are also available.

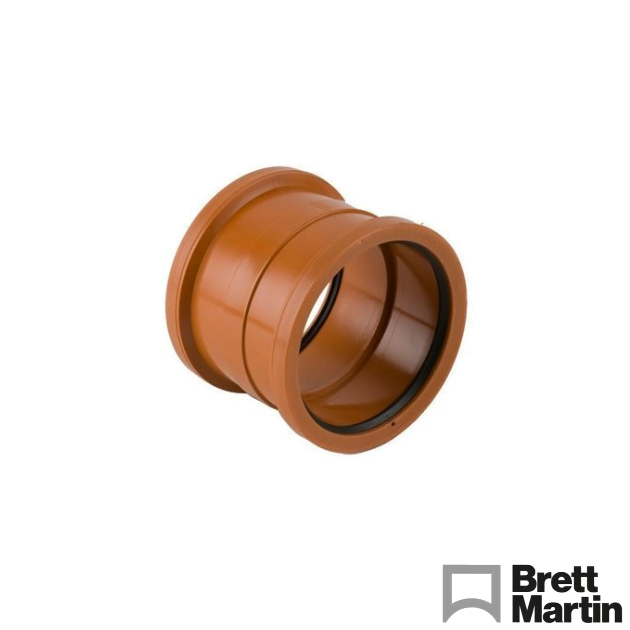
- Drainage Pipe Couplers – Known as joiners, these connect two lengths of pipe together. Single socket versions are available when adapting to solvent systems.

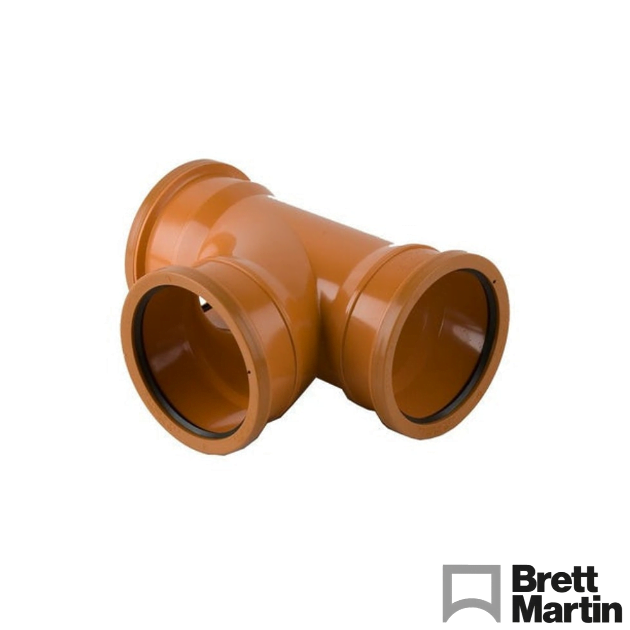
- Drainage Pipe Junctions – Allow splitting or joining of pipe runs. Available as T-junctions (90-degree turns) or Y-junctions (45-degree turns). Double or triple socket options are available.

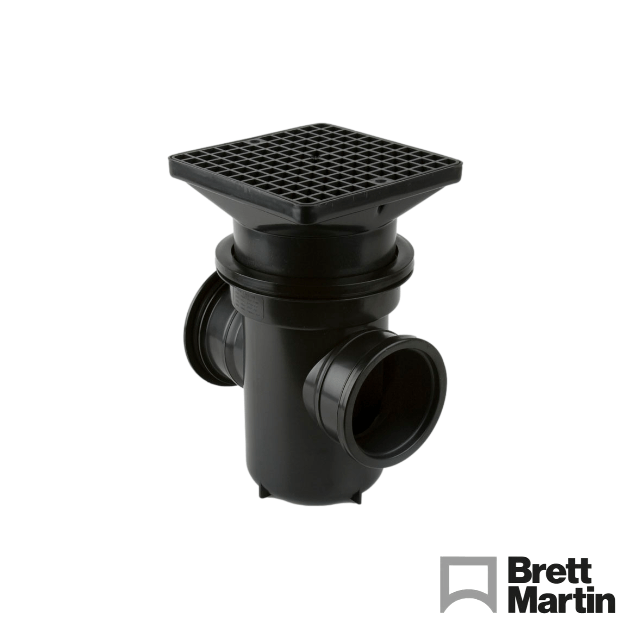
- Bottle Gullies – Feature a grill on top for accepting rainwater downpipes or waste pipes. Built-in traps prevent smells and gases from entering the building.

- Underground Drainage Hoppers – Similar to gullies, these allow downpipes or waste pipes into the underground system but lack built-in traps.
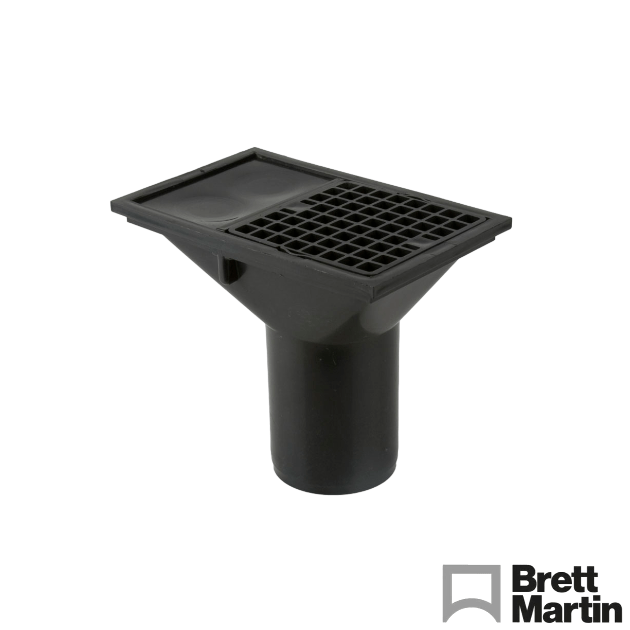

- Lowback P Traps – Installed using hoppers to create traps preventing foul-smelling gases from entering the property.
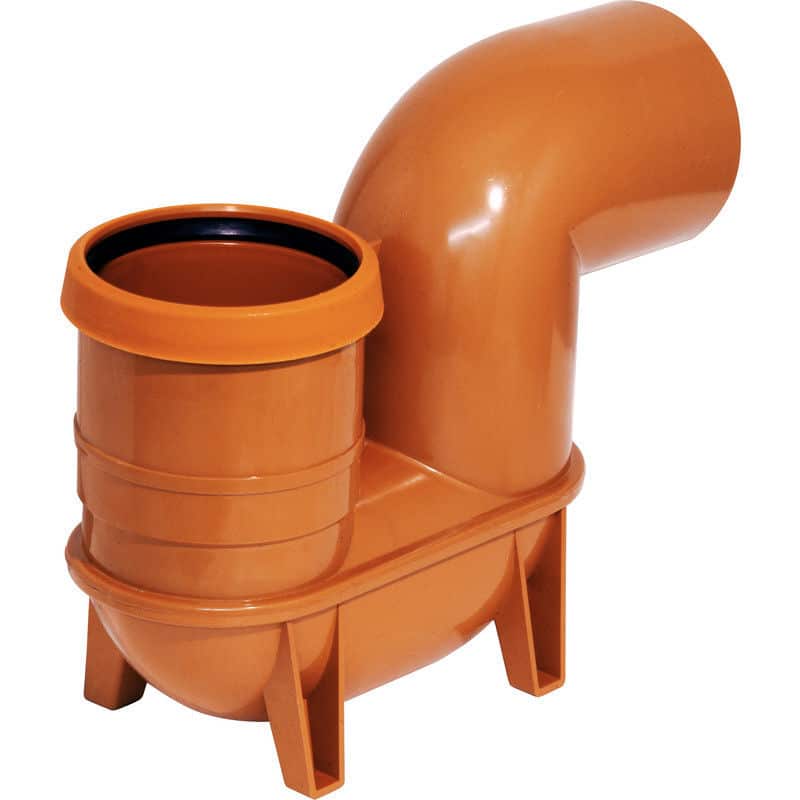

- Rodding Eyes – Installed to facilitate rodding in case of blockages.
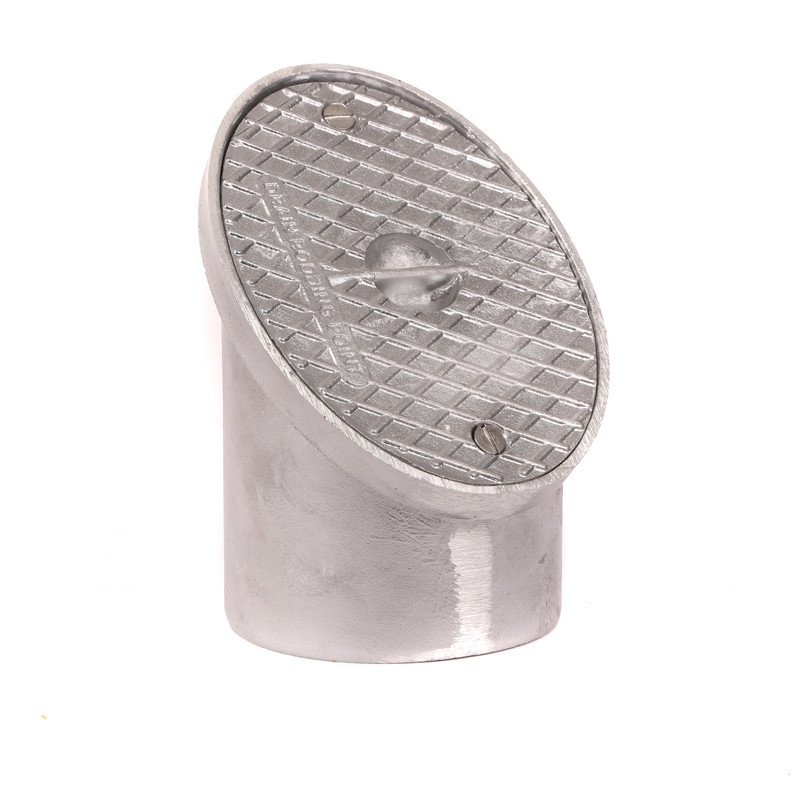

- Universal Rainwater Adaptors – Rubber adapters allowing connection from rainwater downpipes to the underground system.
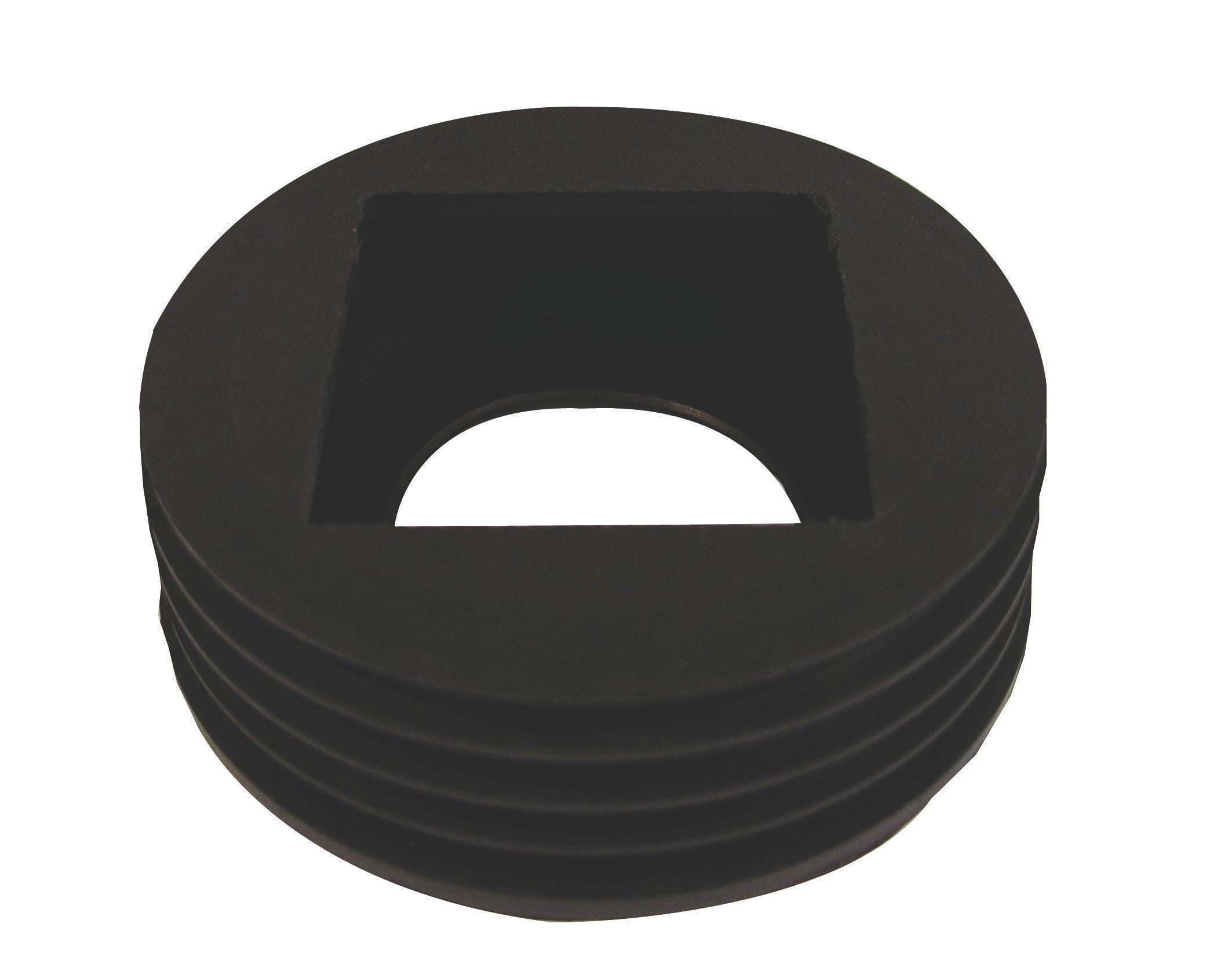

- Manhole Bases, Risers and Lids – Manhole bases allow connections from properties or multiple properties to combine into one run leading to the main sewage system. Typically installed at the end of driveways before entering roads.

Invert levels and falls in underground drainage:
Typically, 110mm drainage pipe is laid with a minimum fall of 1 in 40. This is usual for installations involving five houses or fewer. This ensures sufficient flow to carry waste and water quickly enough to minimize blockages. The same rule applies regardless of the manufacturer or brand. For more details, refer to the Approved Document H – Drainage and Waste Disposal document, but always consult a drainage engineer or local authority if in doubt.
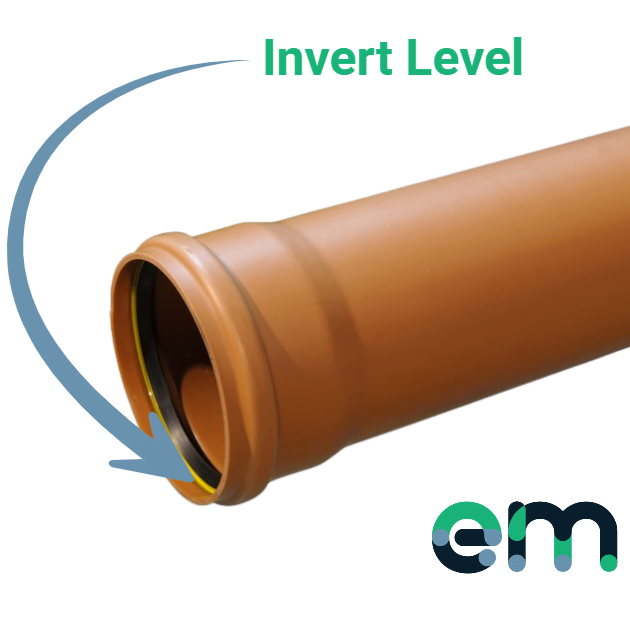
What does invert level mean?
The "invert level" refers to the level of the bottom of the drainage pipe or manhole base outlet. It indicates the level at which water will flow. On architects' or drainage engineers' drawings or plans, the invert level is usually mentioned alongside the cover levels. The invert level is the lowest point inside the pipe where water flows.
The cover level simply refers to the ground level once finished, a good way to remember this is where the manhole cover would go. An invert depth calculation involves subtracting the invert level from the cover level. For instance, if the cover level is 50 and the invert level is 45, the result would be 5 (50 – 45 = 5). These calculations and measurements are crucial for the design and proper functioning of the drainage system.

What are the falls and gradients for underground drainage?
The fall simply means the slope of the pipe. The pipe system needs a fall to allow gravity to move the waste along the pipe. Technically speaking, the fall of the pipe represents the angle and distance it drops vertically along its horizontal length. A calculation is required to determine the correct fall to ensure adequate flow rates and prevent blockages caused by solids or waste. The fall simply means the vertical drop from the start to the end of the pipe run.
A common fall would be 1 in 40, meaning for every 40 units of pipe length, it drops by one unit. For a 40-meter run of pipe, the end of the run would be 1 meter lower than the start. The scale and effect remain the same regardless of whether the unit is meters, centimeters, inches, or any other measurement.
Sometimes the fall is referred to as "the gradient" (though less commonly these days). When calculating a gradient, the calculation differs slightly. Divide the vertical fall by the horizontal length of the pipe run. In our 1 in 40 example, the calculation would be (1 divided by 40) resulting in a gradient of 0.025. See the picture below for reference.
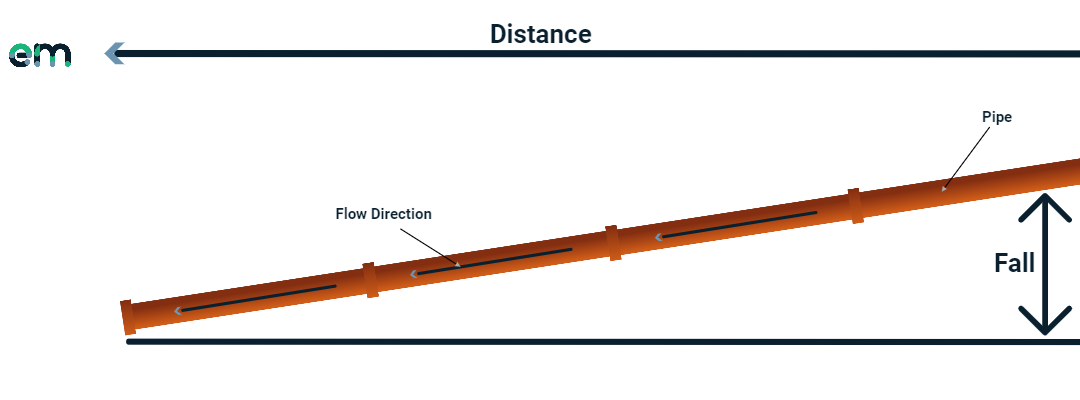
The gradient equals the fall distance.
For example, in a 24-meter section of drainage pipe with a fall of 0.30 meters and asked to calculate the gradient:
- Gradient = 0.30 divided by 24
- Gradient = 0.0125
This can be converted into a gradient written as a ratio or 1
- Gradient = 1 / 0.0125 = 80
- Fall = 1 in 80
The above formula may be rearranged for Fall if the Gradient is known:
The fall is the gradient multiplied by the fall distance
For example, calculate the fall in a 50-meter section of foul water pipework if the gradient is to be 1 in 80. Convert a gradient of 1 in 80 to a number instead of a ratio.
1 / 80 = 0.0125
Fall = Gradient multiplied by Distance
Fall = 0.0125 multiplied by 50
Fall = 0.625 meters or 625mm.
Adapting to other materials
You can adapt PVC drainage to clay or cast iron drainage pipes using rubber pipe connectors featuring a jubilee clip to tighten and adapt to pipes with varying wall thicknesses.
How and when to test the drains?
Although it depends on the local approving authority, you can refer to the Approved Document H – Drainage and Waste Disposal.
What is an OD / ID?
This refers to the outside diameter and inside diameter of the pipe. If connecting or adapting to the pipe, the OD will be the measurement you need. To calculate flow rates, you'll use the ID. The outside diameter minus the inside diameter gives you the wall thickness of the pipe. The inside diameter provides the space within the pipe, while the outside diameter tells you the overall width so you know the size of the hole to drill, etc.
Can I buy this stuff from EasyMerchant?
Yes, and you won't find it cheaper anywhere else! We buy in bulk quantities of this stuff because we can and because of the volumes we purchase, we receive large discounts, enabling us to sell these items at the same price a national contractor would pay. Check out our underground drainage range here. We offer two brands: Brett Martin, a well-known brand for those who prefer or require it, and an eco-friendly brand that performs well and is more affordable.
As always, thank you for reading our guide here at EasyMerchant. If you have any further questions about underground drainage installation, you can call me on 01371 850 120, or email at [email protected]
Author Bio
Nathan Wilde

Nathan has been in the drainage and plastics industry for over 12 years. Having worked for both builders’ merchants and major manufacturers, Nathan has amassed significant industry and product knowledge. At EasyMerchant, Nathan is dedicated to making tradespeople’s lives easier.
Shop Underground Drainage

110mm Drainage Pipe Fittings

110mm 3m Single Socket Underground Drainage Pipe

110mm Drainage Pipe Coupler

110mm Underground Drainage Pipe Junction
Octagonal Ring Joint Gasket,Octagonal Ring Gasket,Octagonal Rtj Gasket,Octagonal Ring Joint
WENZHOU JINGWEI SEAL TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD , https://www.ringjoint-gasket.com
